Paper 3
Course Highlights:
General Studies (GS) Paper 3 for UPSC: A Comprehensive Guide – AAKAR IAS
Introduction:
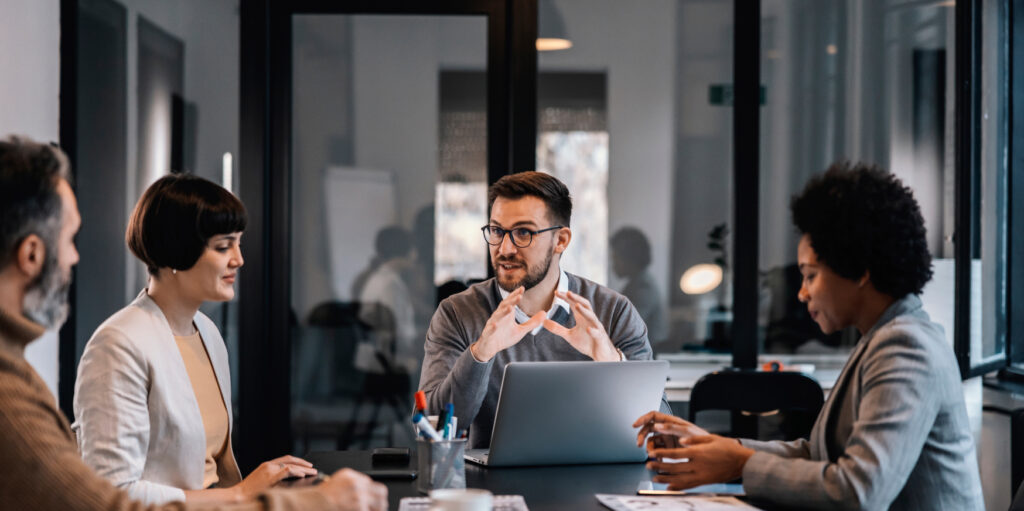
General Studies Paper 3 of the UPSC Civil Services Mains Examination (CSE) is a pivotal paper that evaluates an aspirant’s understanding of key issues related to economics, environment, security, disaster management, and technology. This paper is critical for the aspirant’s overall performance, as it covers significant dimensions of governance and challenges faced by India in its development trajectory.
At AAKAR IAS, we provide in-depth guidance, meticulously structured study resources, and mentorship that helps aspirants master the extensive syllabus of GS Paper 3. We ensure a comprehensive approach to these crucial topics, helping students not only understand the theory but also apply it effectively in the examination.
GS Paper 3 Syllabus Overview:
The GS Paper 3 syllabus is broadly divided into the following key sections:
Economic Development
Agriculture
Environment, Ecology, and Biodiversity
Science and Technology
Security and Disaster Management
1. Economic Development:
This section tests the candidate’s understanding of economic concepts and India’s development challenges. It covers a wide range of topics, from macroeconomic policies to sector-specific growth.Key Topics:
Economic Reforms and Policies:
Economic reforms since 1991, including liberalization, privatization, and globalization (LPG).
Major government schemes for economic development: Make in India, Digital India, Start-up India, Skill India.
Economic growth, GDP, inflation, and unemployment trends.
Government policies related to industrialization, trade, and investment.
Growth and Development:
Inclusive growth, poverty reduction, and regional disparities in growth.
Social and human development indicators: education, health, gender equality, etc.
Challenges related to job creation, agricultural distress, and inequality.
Indian Economy:
Structure and performance of the Indian economy.
Key economic sectors: Agriculture, Industry, Services, and their interlinkages.
Monetary policy and its impact on the economy (Reserve Bank of India, interest rates, inflation targeting).
Fiscal policy and its tools: Taxation, government spending, and budgetary processes.
External sector: Foreign trade, balance of payments, foreign direct investment (FDI), and exchange rates.
Economic Planning:
Five-year plans and the planning process in India.
NITI Aayog and its role in policy formulation.
Sustainable development goals (SDGs) and their alignment with India’s policies.
2. Agriculture:
Agriculture is a critical component of India’s economy and development. This section evaluates the aspirant’s understanding of agricultural policies, practices, and their challenges in India.Key Topics:
Agricultural Policy and Reforms:
Government policies related to agriculture (National Agriculture Policy, Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana, PM-KISAN, etc.).
Agricultural credit, insurance, and subsidies.
Issues related to land reforms and land acquisition.
Agriculture and Rural Development:
Role of agriculture in rural development and employment.
Agricultural marketing and supply chains: MSP (Minimum Support Price), APMC (Agricultural Produce Market Committees), and e-NAM (National Agriculture Market).
Food security and government initiatives like the Public Distribution System (PDS).
Technology in Agriculture:
Use of biotechnology, GM crops, and innovations in agricultural practices.
Role of ICT and digital technology in agriculture.
Sustainable farming practices: Organic farming, water conservation, and agroforestry.
Challenges in Agriculture:
Impact of climate change on agriculture and adaptation strategies.
Problems of smallholder farmers: low productivity, poor access to markets, and high indebtedness.
Issues in the agricultural labor force: migration, skill development, and rural unemployment.
3. Environment, Ecology, and Biodiversity:
This section evaluates the candidate’s awareness and understanding of environmental issues, conservation efforts, and the balance between development and ecological sustainability.Key Topics:
Environmental Impact:
Environmental degradation: deforestation, soil erosion, air and water pollution.
Greenhouse gases, climate change, and the role of India in global climate agreements (e.g., COP21, Paris Agreement).
Conservation and Biodiversity:
India’s rich biodiversity: flora and fauna, and biodiversity hotspots.
Conservation policies: Protected areas, wildlife sanctuaries, national parks, and conservation of endangered species.
Biodiversity conservation programs: National Biodiversity Action Plan (NBAP), Project Tiger, Project Elephant, etc.
Environmental Laws and Policies:
Environmental regulations in India (e.g., Environmental Protection Act, Forest Conservation Act, Wildlife Protection Act).
Environmental impact assessment (EIA) process and its significance.
Sustainable Development:
The concept of sustainable development and its relevance in India’s growth model.
Renewable energy, energy conservation, and India’s transition to clean energy.
Waste management, recycling, and circular economy concepts.
Ecology and Ecosystem Services:
Importance of ecosystems and ecosystem services for human welfare.
Role of forests, wetlands, rivers, and oceans in maintaining ecological balance.
4. Science and Technology:
Science and Technology are vital for India’s progress, and this section assesses an aspirant’s knowledge of developments in these fields and their implications for governance and policy.Key Topics:
Science and Technology in India:
Achievements in space technology, nuclear energy, and defense technology (e.g., ISRO, DRDO).
Role of innovation, start-ups, and research institutions (e.g., IITs, CSIR).
Health and Biotechnology:
Advances in biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, and health-related innovations.
Issues like drug resistance, vaccines, and public health initiatives (e.g., National Health Policy, Ayushman Bharat).
Technology for Development:
Digital India initiative and the role of IT in governance and development.
Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, and automation.
Cybersecurity challenges, data privacy issues, and related laws (e.g., Data Protection Bill).
Emerging Technologies:
Innovations in agriculture, energy, and industry due to technological advances.
Use of big data, cloud computing, and machine learning in governance.
Sustainable technologies for clean energy and green growth.
Science and Technology Policy:
India’s Science and Technology Policy and its vision.
Role of public and private sectors in the promotion of scientific research and innovation.
5. Security and Disaster Management:
This section evaluates the aspirant’s understanding of internal and external security challenges and disaster management practices in India.Key Topics:
Internal Security:
Challenges related to terrorism, Naxalism, insurgencies, and communal violence.
Role of agencies like the Intelligence Bureau (IB), National Investigation Agency (NIA), and Central Armed Police Forces (CAPFs).
Border Security and National Security:
India’s national security framework and key security challenges (e.g., border disputes, cross-border terrorism).
Role of the Indian Army, Navy, and Air Force in national defense.
Disaster Management:
Natural disasters in India: Floods, cyclones, earthquakes, droughts, etc.
National Disaster Management Policy and the role of National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA).
Strategies for disaster preparedness, mitigation, and response.
Climate change-induced disasters and resilience-building measures.
Books and Resources for GS Paper 3:To perform well in GS Paper 3, candidates need a combination of theory and current affairs updates. Here are some essential resources:
Economic Development:
“Indian Economy” by Ramesh Singh.
“Indian Economy: Performance and Policies” by Uma Kapila.
Economic Survey and Union Budget (Annual Publications).
Agriculture:
“Indian Agriculture” by K.R. Gupta.
“Agriculture in India” by S.S. Johl.
Reports from the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
Environment and Ecology:
“Environment and Ecology” by Majid Husain.
“Shankar’s IAS Environment” (for Ecology and Biodiversity).
National Forest Policy and National Biodiversity Action Plan (available online).
Science and Technology:
“Science and Technology” by Ravi P. Agrahari.
Science Reporter magazine.
The official websites of ISRO, DRDO, Ministry of Science & Technology for updates.
Security and Disaster Management:
“Internal Security” by Ashok Kumar and S. K. Singh.
“Disaster Management” by G.K. Kapoor.
National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) guidelines and reports.
How AAKAR IAS Helps in GS Paper 3 Preparation:Comprehensive Study Plan:
We offer a structured study plan for GS Paper 3, ensuring that all sections are comprehensively covered, with focus on theory and application.
Expert Faculty:
AAKAR IAS provides guidance from faculty with years of experience in training UPSC aspirants. Our experts break down complex topics and offer real-world applications of theoretical concepts.
Why Choose Aakar ICS?
At Aakar ICS Coaching, we offer a range of courses designed to cater to the diverse needs of ICS aspirants. Whether you are just starting your preparation or looking to fine-tune your skills, we have the right course for you.
- Time Tested Learning Pedagogy
- Personal Mentorship
- Highest Success Rate
Courses
aakariaslucknow@gmail.com
Phone Number:
0522-4044438, +91 9519483938 +91 9415999194
Our Address:
B-59, Sector-H, Opp.-Axis Bank, Near Puraniya Chauraha, Aliganj, Lucknow-226024