Paper 2
Course Highlights:
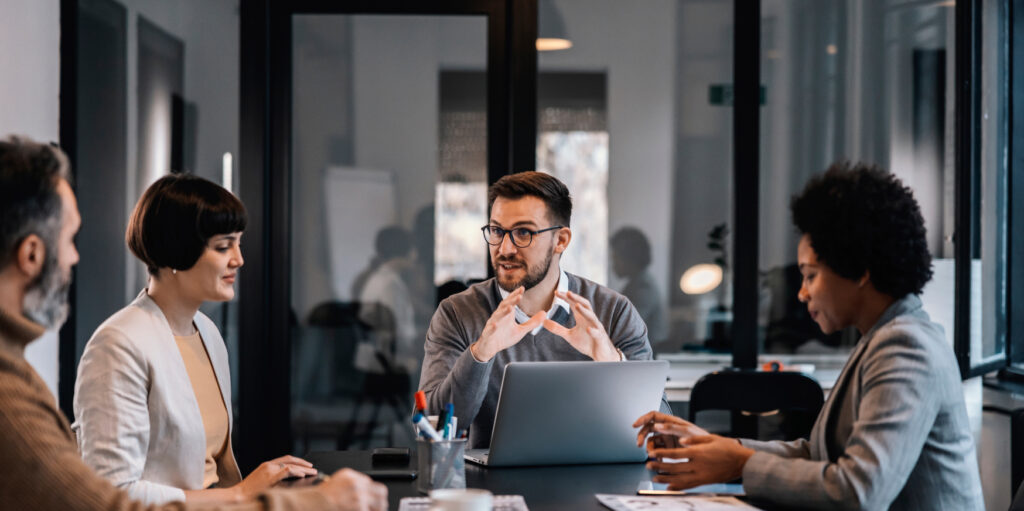
General Studies (GS) Paper 2 for UPSC: A Comprehensive Guide – AAKAR IAS
Introduction:
General Studies (GS) Paper 2 of the UPSC Civil Services Mains Examination (CSE) is crucial for every aspirant aspiring to join the Indian Administrative Service (IAS). This paper focuses on Governance, Constitution, Polity, Social Justice, and International Relations. It tests an aspirant’s knowledge of the Indian political system, the Constitution of India, the functioning of various institutions, and contemporary issues related to governance and international affairs.
At AAKAR IAS, we provide expert guidance and a structured approach to help aspirants master the diverse topics covered in GS Paper 2, ensuring a deep understanding of concepts and effective answer-writing techniques. Our comprehensive resources and mentorship support candidates to excel in this paper.
GS Paper 2 Syllabus Overview:
The syllabus for GS Paper 2 is divided into the following major sections:
Polity and Governance
Constitution of India
Social Justice
International Relations
1. Polity and Governance:
This section focuses on the political system, institutions of governance, and processes of law-making, administration, and service delivery in India. It tests the candidate’s understanding of political dynamics, both at the center and the states.Key Topics:
Indian Constitution:
Historical background, framing of the Constitution, and Preamble.
Fundamental Rights, Fundamental Duties, and Directive Principles of State Policy.
Union and State Legislatures: Structure, powers, and functions.
Union and State Executive: Powers and functions of the President, Prime Minister, Council of Ministers, Governor, and Chief Minister.
Judiciary: Supreme Court, High Courts, Judicial Review, and Judicial Independence.
Amendments to the Constitution and the process of constitutional change.
Public Administration and Governance:
Role of the Civil Services and Administrative Reforms.
Issues related to accountability and transparency in governance: RTI (Right to Information), Lokpal, and Lokayuktas.
Corruption, transparency, and accountability: Mechanisms and legal provisions.
Governance challenges: Federalism, decentralization, and the role of the states.
Election Commission, E-Governance, and Technology in governance.
Federal Structure and Center-State Relations:
Distribution of powers between Union and States: Legislative, executive, and financial relations.
Role of inter-State Council, Zonal Councils, and other institutions.
Role of the President in emergency situations (National, State, and Financial Emergencies).
Institutional Framework and Development:
Parliamentary system: Role and working of the Parliament.
Political parties, elections, and electoral reforms in India.
Role of the media in Indian democracy and its impact on governance.
2. Constitution of India:
The Constitution of India is the cornerstone of Indian governance and the rule of law. This section involves understanding the Constitution’s provisions, important judicial pronouncements, and significant amendments.Key Topics:
Constitutional Provisions:
Federalism, Parliamentary system of government, and separation of powers.
Fundamental Rights and their application.
Role of the President, Prime Minister, and Parliament in governance.
Emergency provisions and President’s Rule.
Constitutional bodies: Election Commission, Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG), Finance Commission, etc.
Non-constitutional bodies: National Human Rights Commission (NHRC), Central Information Commission (CIC), etc.
Judiciary and Judicial Review:
Supreme Court: Jurisdiction, powers, and functions.
Judicial Review and its scope.
The collegium system and judicial appointments.
Landmark judgments and their impact on Indian society and governance.
Amendments and Reforms:
Key amendments to the Constitution and their significance (e.g., 42nd, 44th, and 73rd Amendments).
Debate on Constitutional reforms, issues with the functioning of the Constitution, and areas requiring reforms.
3. Social Justice:
This section tests your understanding of social justice issues and government initiatives aimed at ensuring social equity, inclusion, and empowerment of marginalized communities. It focuses on issues related to poverty, inequality, healthcare, education, and affirmative action.Key Topics:
Social Justice and Welfare:
Concept of Social Justice in India.
Poverty, inequality, and the role of government in poverty alleviation.
Issues concerning marginalized communities: SCs, STs, OBCs, and women.
Government schemes and programs for social justice (e.g., MGNREGA, PMAY, Beti Bachao Beti Padhao).
Social Protection Mechanisms:
Rights-based approaches to social justice.
Social welfare schemes for vulnerable populations (e.g., health insurance schemes, food security).
Role of NGOs and civil society in promoting social justice.
Rights and Affirmative Action:
Constitutional provisions related to affirmative action (reservation, SC/ST/OBC welfare).
Laws and policies related to the protection of women, children, and minorities (e.g., Domestic Violence Act, Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, etc.).
Disability rights, senior citizens, and other vulnerable groups.
Healthcare and Education:
Right to Education (RTE) and Right to Health.
Government efforts to improve education and healthcare in India.
Challenges in delivering social justice in health and education sectors.
Environmental and Developmental Issues:
Sustainable development and its link to social justice.
Challenges of inclusive growth and environmental protection.
Climate change and its impact on social justice.
4. International Relations:
This section tests the candidate’s knowledge of India’s foreign policy, international relations, and global organizations. The emphasis is on the country’s diplomatic relations, security concerns, and participation in global institutions.Key Topics:
India’s Foreign Policy:
Evolution of India’s foreign policy and its guiding principles.
India’s relations with major global powers (USA, Russia, China, EU, etc.).
India’s neighborhood policy: Relations with neighboring countries like Pakistan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Nepal, etc.
India’s role in global organizations: United Nations (UN), BRICS, G20, World Trade Organization (WTO), etc.
India’s engagement with multilateral and regional groupings (ASEAN, SAARC, BIMSTEC, etc.).
Global Issues:
Global challenges: Terrorism, Climate Change, Nuclear Non-Proliferation, and Cybersecurity.
India’s role in addressing global security issues: Peacekeeping, counter-terrorism, and non-alignment.
India’s foreign trade policy and economic diplomacy.
International Organizations:
Role and structure of key international organizations (UN, WTO, WHO, IMF, World Bank, etc.).
India’s contributions and challenges in these organizations.
Diplomatic Initiatives:
India’s bilateral, regional, and multilateral diplomatic initiatives.
Trade agreements, diplomatic treaties, and cooperation frameworks.
Indian diaspora and its role in foreign policy.
Books and Resources for GS Paper 2:To excel in GS Paper 2, students should refer to a mix of standard textbooks, current affairs, and reports. Here are some of the recommended books and resources:
Polity and Governance:
“Indian Polity” by M. Laxmikanth.
“Introduction to the Constitution of India” by D.D. Basu.
NCERT books (Class 11 and 12, Political Science).
“Governance in India” by M. Laxmikanth.
Social Justice:
“Social Justice in India” by A. Vaidyanathan.
“Social Problems in India” by Ram Ahuja.
NCERT Sociology books (Class 11 and 12).
International Relations:
“International Relations” by Pavneet Singh.
“India’s Foreign Policy” by Rajiv Sikri.
The Hindu, Indian Express (for current affairs).
Monthly magazines like Yojana, Kurukshetra, and Frontline.
Constitutional Law:
“Indian Constitutional Law” by M.P. Jain.
“Constitutional Law of India” by P.M. Bakshi.
Reports from the Law Commission of India and other constitutional bodies.
How AAKAR IAS Helps in GS Paper 2 Preparation:Structured Study Plans:
AAKAR IAS provides structured study material and guidance to ensure that all topics in GS Paper 2 are covered thoroughly and systematically.
Expert Faculty:
Our team of experts offers clear and concise explanations of complex political and governance-related concepts, ensuring that students build a solid foundation.
Current Affairs Integration:
We help students integrate current affairs with theoretical knowledge, ensuring that answers reflect a balanced understanding of the subject.
Answer Writing and Feedback:
Regular answer writing practice with detailed feedback ensures that students improve their answer quality and presentation, which is essential for scoring well in GS Paper 2.
Mock Tests and Test Series:
We offer mock tests and a comprehensive test series that simulate real exam conditions, helping students manage time and enhance their exam-taking skills.
Why Choose Aakar ICS?
At Aakar ICS Coaching, we offer a range of courses designed to cater to the diverse needs of ICS aspirants. Whether you are just starting your preparation or looking to fine-tune your skills, we have the right course for you.
- Time Tested Learning Pedagogy
- Personal Mentorship
- Highest Success Rate
Courses
aakariaslucknow@gmail.com
Phone Number:
0522-4044438, +91 9519483938 +91 9415999194
Our Address:
B-59, Sector-H, Opp.-Axis Bank, Near Puraniya Chauraha, Aliganj, Lucknow-226024